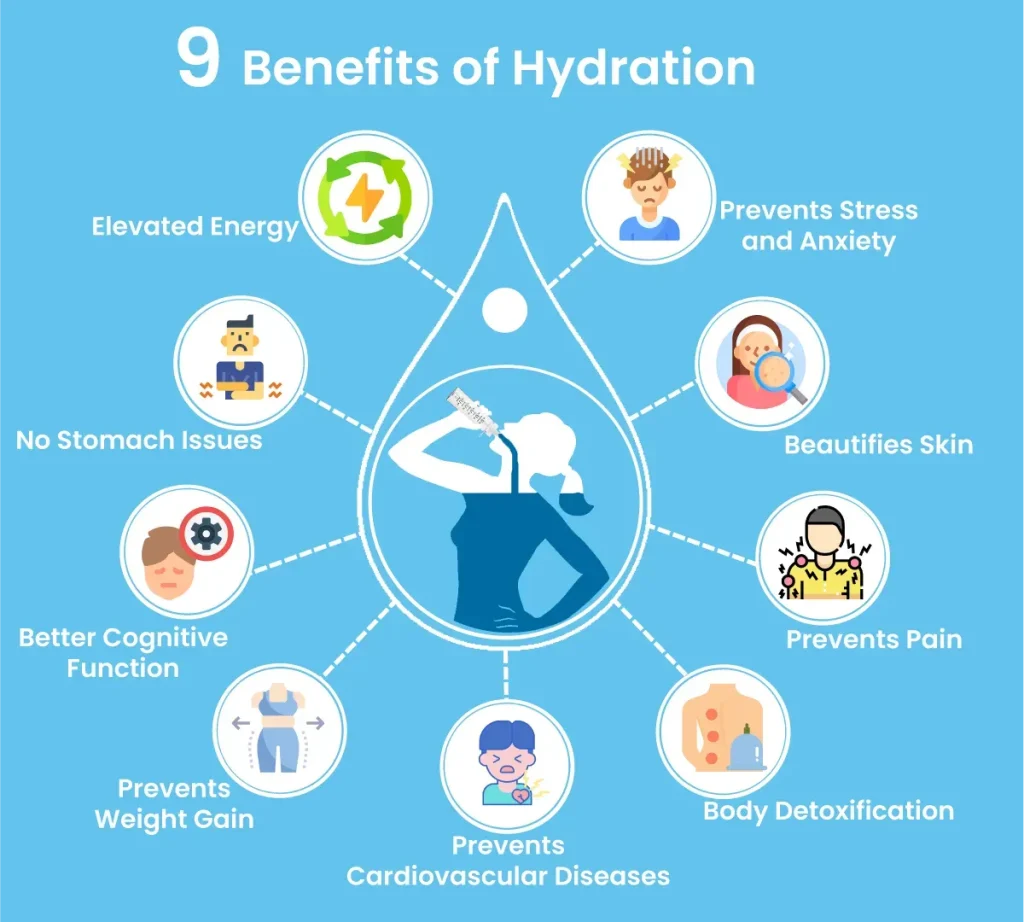
Hydration and Health underpin everyday well-being, shaping energy, mood, and resilience. Following daily water intake guidelines can help you plan consistent sips throughout the day. Even mild dehydration signs can sap concentration and physical performance, underscoring how hydration and athletic performance are linked. When fluids are adequate, you may notice water benefits for energy, focus, and overall vitality. Practical hydration tips for health—such as carrying a bottle, scheduling small drinks, and choosing lower-sugar beverages—make steady intake simple.
Beyond formulas and headlines, the science of proper fluid balance reveals why staying hydrated matters for every body system. In everyday terms, this means paying attention to your hydration status, water intake, and how thirst cues guide intake. Consistent hydration supports kidney function, digestion, temperature regulation, and athletic recovery, reframing hydration as a foundational health habit. From a public health perspective, embracing water-rich foods and low-calorie beverages complements electrolyte balance and cognitive clarity. By viewing hydration as a daily readiness practice rather than a response to thirst, readers can build sustainable, enjoyable routines.
Hydration and Health: Following Daily Water Intake Guidelines for Vital Functions
Water is more than a thirst quencher; it’s a fundamental nutrient that underpins cognitive clarity, digestive efficiency, and steady energy throughout the day. By aligning your routine with daily water intake guidelines, you support nearly every system in the body, helping mood, focus, and resilience. In practice, consistent hydration translates to smoother digestion, balanced metabolism, and a more reliable sense of well‑being, underscoring the water benefits for energy that many people notice even before exercise or formal activity.
Watching for dehydration signs and adjusting habits accordingly is a practical way to protect health. To reinforce hydration and health, adopt simple hydration tips for health: carry a reusable bottle, drink water with meals, and listen to thirst while considering climate and activity. These small adjustments help you meet daily water intake guidelines and prevent early deficits that can sap attention, mood, and daily performance.
Hydration and Athletic Performance: Optimizing Power, Endurance, and Recovery
When you exercise, water becomes a critical ally for joints, temperature control, and blood flow to working muscles. Hydration supports athletic performance by maintaining plasma volume, reducing perceived exertion, and helping the body sustain intensity longer. The water benefits for energy are especially evident during hot weather or high‑intensity sessions, where proper hydration can improve endurance, cognitive focus, and recovery windows after workouts.
To maximize performance, apply a practical hydration framework: pre‑hydrate before workouts, sip water during, and rehydrate afterward, guided by thirst, urine color, and the duration of activity. Ground your plan in daily water intake guidelines and adjust for sweat losses from climate and conditioning. Keep an eye on dehydration signs during training and use hydration tips for health—such as flavoring water, choosing low‑calorie beverages, and moderating caffeine intake—to sustain consistent hydration without overdoing fluids.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do daily water intake guidelines influence Hydration and Health, and what practical hydration tips for health can help me meet them?
Daily water intake guidelines provide a practical framework for Hydration and Health. For many adults, about 3.7 liters (roughly 13 cups) per day for men and 2.7 liters (about 9 cups) for women, with some from food, helps support digestion, energy, and temperature regulation. Practical hydration tips for health include starting the day with water, sipping consistently throughout the day, carrying a reusable bottle, drinking water before meals, and adjusting intake based on thirst, urine color, activity, and climate.
What dehydration signs should prompt me to optimize hydration for Hydration and Athletic Performance and to enjoy the water benefits for energy?
Watch for dehydration signs such as thirst, dark yellow urine, dry mouth, dry skin, headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and reduced sweating during exercise. If you notice these cues, increase fluids promptly and consider electrolyte-containing drinks during intense sweating. Proper hydration supports Hydration and Athletic Performance by improving endurance and reducing perceived effort, while maintaining steady energy levels—emphasizing the water benefits for energy when hydration is consistent around activities.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Water is a fundamental nutrient that supports everyday well‑being, influencing mental clarity, energy, mood, digestion, and resilience. Practical strategies help maintain consistent hydration. |
| The role of water in the body | Supports digestion, nutrient transport, kidney function, temperature regulation, and blood volume. Adequate hydration enhances circulation and oxygen delivery; dehydration impairs performance and function. |
| Hydration and mental performance | Hydration strongly affects cognition. Mild dehydration can cause headaches, reduced concentration, and mood shifts; staying well‑hydrated supports sharper focus, faster thinking, and steadier energy. |
| Hydration and physical performance | Lubricates joints, regulates temperature, and maintains blood flow to muscles. Proper hydration reduces cardiac effort and can improve endurance; severe dehydration increases fatigue, cramps, dizziness, and heat illness risk. |
| Hydration, digestion, and weight management | Aids digestion, prevents constipation, and can influence appetite and energy balance. Thirst is sometimes mistaken for hunger; adequate water helps gauge true hunger cues. |
| Skin health and immune function | Hydration supports skin moisture and barrier function. Internal hydration aids immune function and waste removal; hydration complements sleep and nutrition in supporting overall health. |
| Daily water intake guidelines and practical strategies | Guidelines: roughly 3.7 L/day (men) and 2.7 L/day (women), including fluids from food. Individual needs vary; adjust based on thirst, urine color, activity, climate, and health status. |
| Dehydration signs to watch for | Early signs: thirst, dark urine, dry mouth/skin. Progression: headaches, dizziness, fatigue, reduced sweating. Severe cases: rapid heart rate, confusion, fainting. Seek medical advice if symptoms persist or accompany illness. |
| Hydration tips for health | Carry a reusable bottle, set reminders, and pair hydration with routines. Flavoring can help some people; limit added sugars. Caffeine contributes to intake but can have diuretic effects in excess; balance is key. Increase intake in heat or during intense exercise. |
| Hydration in different life stages and conditions | Needs vary by age, pregnancy/breastfeeding, older age, and climate. Some medical conditions and medications affect balance. Consult a healthcare provider as needed; practice mindful hydration and plan around activity. |
| Practical hydration framework for everyday life | Start the day with water; sip consistently; pair with activity (before/during/after workouts); include nutrient‑dense fluids when appropriate; monitor urine color as a hydration indicator. |
Summary
Conclusion: The topic of Hydration and Health highlights how consistent, mindful fluid intake supports cognitive function, physical performance, digestion, skin integrity, and immune resilience. By understanding your body’s signals and applying simple strategies—starting the day with water, sipping throughout the day, and adjusting for activity and climate—you can optimize energy, mood, and long‑term well‑being. Hydration and Health is a daily practice that aligns everyday choices with enduring health goals.