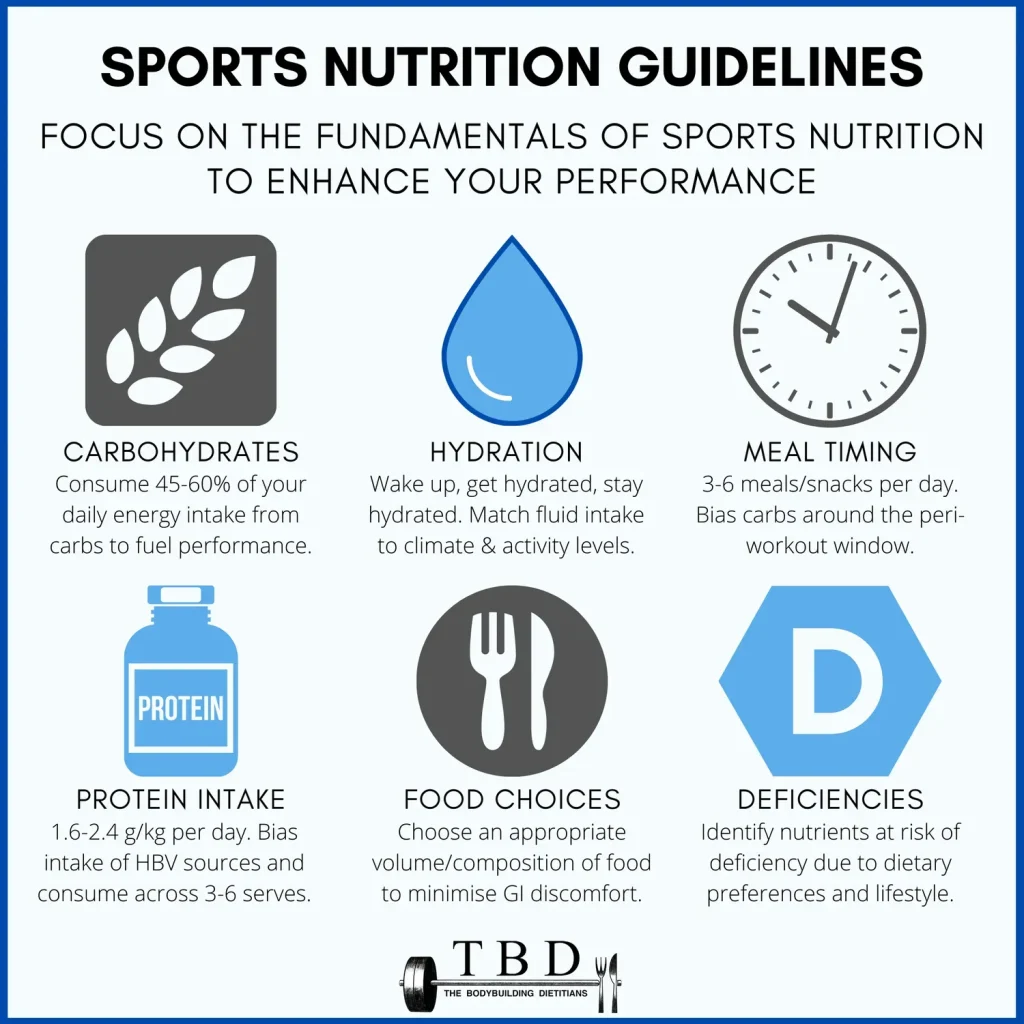
Sports nutrition essentials form the backbone of athletic performance, shaping how athletes fuel for training and competition. Whether you are a competitive runner, a gym enthusiast, or a weekend warrior, what you eat matters as much as how you train. This guide emphasizes practical strategies to support energy, endurance, and recovery. A balanced mix of protein, carbohydrates, fats, and fluids helps sustain performance and daily well-being. With clear guidelines and real-world meal ideas, you can turn knowledge into action and fuel your best results.
In other terms, athlete fueling hinges on carbohydrate timing for athletes, pre-workout nutrition, protein balance, and smart fluid strategies to support training and competition. This perspective reflects a broader language of sports nutrition, with terms like fueling for performance, glycogen restoration, and recovery-oriented meal planning. Hydration strategies for athletic performance are essential, guiding fluid intake and electrolyte replacement during and after workouts. Together, these ideas translate into practical routines you can apply on busy days to sustain energy, support recovery, and drive consistent progress.
Sports nutrition essentials for peak performance
Sports nutrition essentials for peak performance start with a simple truth: energy comes from carbohydrates, protein, and fats, but timing and balance determine how those macronutrients support training. This approach aligns with peak performance nutrition by emphasizing when you eat as much as what you eat, so your body has fuel during hard efforts and recovery afterward. For most athletes, a carbohydrate-rich meal the night before a demanding session, a light pre-workout nutrition snack, and a carbo-protein post-workout meal create a predictable rhythm that sustains energy, supports endurance and strength, and speeds recovery. Hydration is the silent partner in this equation, ensuring fluids and electrolytes are ready when you need them.
To translate sports nutrition essentials into daily practice, plan meals around training windows and distribute protein evenly through the day. A practical template includes 30-60 g of carbohydrates and 10-30 g of protein 1-3 hours before training, a carbohydrate-inclusive post-workout meal soon after exercise to replenish glycogen and kick-start recovery, and consistent protein intake across meals to sustain muscle protein synthesis. Hydration strategies for athletic performance should be woven into every session—start well hydrated, drink according to thirst and sweat rate, and adjust electrolytes for heat or long efforts. By pairing pre-workout nutrition, carbohydrate timing for athletes, and post-workout recovery meals, you build a reliable foundation for ongoing improvement.
Carbohydrate timing for athletes and hydration strategies for athletic performance
Carbohydrate timing for athletes is the art of aligning fuel delivery with training demands to maximize glycogen stores and minimize fatigue. On high-volume or high-intensity days, increase carb availability around workouts; on lighter days, lean on fats while preserving protein. Endurance sessions benefit from breakfast- and pre-workout meals rich in complex carbs, while strength or sprint sessions benefit from targeted carbohydrates in the minutes before and after training. This carbohydrate periodization helps the body store glycogen when needed and avoid unnecessary caloric excess on rest days.
Practical hydration strategies for athletic performance accompany this timing approach. Start each session well hydrated, drink fluids to match sweat losses, and use electrolytes for longer efforts or hot conditions. After training, rehydrate with water and electrolytes, then pair a post-workout recovery meal to speed glycogen replenishment and muscle repair. For everyday planning, combine a sensible pre-workout nutrition option with a carb-forward post-training meal and a protein-focused meal later, ensuring every training day fuels adaptation and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do sports nutrition essentials, including peak performance nutrition and pre-workout nutrition, support training and competition?
Sports nutrition essentials provide the framework for fueling training and competition. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for most athletes, while protein supports muscle repair and recovery after stress; fats offer a steady energy reserve. A practical pre-workout nutrition plan is to consume 30-60 g of carbohydrates and 10-30 g of protein 1-3 hours before training, with modest fats to keep digestion comfortable. The concept of peak performance nutrition emphasizes timing and balance around workouts—think carb-rich meals the night before, a light, protein-containing snack before training, and a carb-inclusive meal after training to restore glycogen and spark recovery.
What are practical hydration strategies for athletic performance and how should carbohydrate timing for athletes be planned around workouts?
Hydration strategies for athletic performance start with being well-hydrated before you train. Aim for roughly 5-7 ml/kg 2-4 hours before exercise and include electrolytes when sessions exceed an hour. During workouts, drink to match sweat losses, typically 150-350 ml every 15-20 minutes, and rehydrate afterward to restore body weight. Carbohydrate timing for athletes should align intake with training demands: higher-carb around high-volume or high-intensity days to replenish glycogen, and moderate carbs on lighter days; this carbohydrate periodization supports performance and recovery.
| Section | Key Points | Practical Tips | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Science of fueling |
|
|
||||||||||||
| Pre‑workout nutrition |
|
|
||||||||||||
| Carbohydrate timing for athletes |
|
|
Hydration strategies for athletic performance |
|
|
Protein intake and distribution |
|
|
Post‑workout recovery meals |
|
|
Meal planning and daily templates |
|
|
Summary
Sports nutrition essentials underpin peak athletic performance by providing a practical framework of timing, balance, and variety. Fueling consistently with pre-workout nutrition, carbohydrate timing for athletes, hydration strategies, adequate protein, and thoughtful post-workout recovery meals supports endurance, strength, and faster recovery across workouts and seasons. Use the ideas and sample meal ideas to design a plan that fits your sport, schedule, and preferences. Remember that small daily choices add up to big performance gains over time. For personalized guidance, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist to tailor the plan to your training program and goals.